IGF-1 Definition
IGF-1 is short for Insulin-like Growth Factor 1, which can be translated asinsulin-like growth factor 1. Also known as somatomedin C, this hormone is mainly produced by the liver through its stimulation by growth hormone. It is released into the bloodstream.
Indeed,IGF 1 is a growth factor, but it is necessary to have the right level, a too low or too high level can be a source of problems. IGF 1 plays a leverage role in children’s growth, and clinical studies have shown that milk proteins have a significant effect on plasma IGF 1.
It is even considered that the size evolution of the “young”, in increase in many countries, is at the origin of an important consumption of milk and derived products, due to the proteins it contains.
Regular physical activity or sport practiced intensively reduces the body’s production of IGF 1 and increases its fixation in the blood (via IGF BP), thus limiting the loss of bone density that occurs with age.
Effects of doping with IGF-1
Insulin-like Growth Factor 1, Somatomedin. This product is supposed to produce the same effects as insulin, as an anabolic, is this the case? Let’s go into a little more detail…
For several years now, everyone has been talking about the hormone IGF-1 in gyms, fitness clubs and specialized magazines.
IGF is a growth factor identical to insulin, it is also called somatomedin C. Its role is extremely important in the growth of young children, and for adults, it plays an anabolic role.
It is the growth hormone that conditions its activation. This growth hormone triggers the action of the liver, which produces the hormones that are responsible for muscle growth. One of these hormones is IGF-1,
IGF-1 has a much more direct action than growth hormone itself. It is therefore easy to understand the keen interest that all body-builders and other “weight lifters” may have
What are the effects of the hormone IGF-1 for athletes who practice bodybuilding?
- It causes bone and muscle growth
- It has an anabolic role, meaning that it is a substance that increases anabolism, in other words nutrients transformation into living tissue.
- The IGF1 hormone also brings a real improvement in recovery and also in healing, it also reduces fat mass.
It is important to point out that growth hormone makes the whole body and therefore all the muscles bigger. It is useful and necessary to draw attention to the fact that the body can become deformed. It is quite easy and straightforward for a specialist to identify an athlete who consumes this type of product.
The human growth hormone IGF 1 has many positive effects. It causes muscle building by increasing cells (hyperplasia), whereas anabolic steroids will simply increase the muscle size of existing cells.
This means that even after you stop taking it, you will continue to progress.
Few studies have been conducted on IGF LR3 (as opposed to IGF 1), which is known to be 2 to 3 times more potent than standard IGF 1 due to its longer half-life.
IGF 1 is rarely used because it has a very short life span plus at least 10 minutes. Its substitute, IGF-1 LR3 (a modified version of IGF-1, which is not naturally produced by the body) is widely preferred, with a duration of use of up to several hours. As a result, it is taken less frequently and in smaller quantities in freeze-dried or already reconstituted form.
Its dosage ranges from 20 to 120 mcg/day. The results are visible quite quickly. The duration of the treatment varies from 4 weeks to 50 days. The ideal intake is an intramuscular injection just after training.
A study on male subjects who injected themselves daily, over a period of 6 weeks (either with HGH alone, IGF-1 alone or IGF-1 + HGH together), shows an increase in lean body mass, increased stamina as well as a decrease in fat mass.
PEG-MGF (growth factor)
A scientific report shows the doping potential of this product. A first study had shown that a single injection on a mouse muscle had allowed the growth of 25% of it, in only 3 weeks.

Side effects of IGF-1
Hypoglycemia: Hypoglycemia can cause dizziness and lightheadedness. This can be compensated by a balanced diet and carbohydrate intake soon after the injections
Water retention: some users have demonstrated the characteristic of water retention. As the excess is fixed in the tissues, the body stores more water than it eliminates.
Nutrition during an IGF-1 treatment
IGF-1 peptides are not influenced by food. There are no diet constraints or dietary modifications to be made.
The only “rules” for IGF-1 peptides are totry to do the injections as soon as possible after training, and if possible in a muscle, so that localized muscle strengthening can begin to occur immediately. However, if you can’t follow these rules don’t worry, because the long half-life of both peptides means that your injections will still travel through the bloodstream and find receptor sites in the muscles to carry out their anabolic effects.
Since the primary role of IGF-1 and PEG-MGF is to create new muscle cells, the best diet is a high protein diet, preferably taken around workouts.
The most important time to consume these proteins, preferably in the liquid form of amino acids such as BCAAs, is immediately before the session and also during your workout.
In fact, in a very logical way, the protein taken after training does not contribute to the synthesis of muscle proteins, but to the total protein synthesis of the body, and the consumption of amino acids during a training session leads directly to muscle protein synthesis due to the faster circulation of blood because of the effort produced, thus leading to the More efficient delivery of amino acids directly to the muscles.

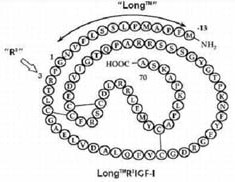
There are also variants, with theIGF-1 DES. Its effectiveness would be 10 times greater than that of normal IGF-1.
IGF-1, in its natural (endogenous) version, is composed of 70 amino acids. DES (1,3) IGF-1 has undergone a modification in its “sequence”, the last 3 amino acids (N-terminal tri-peptide) have been deleted.
With this modification, IGF-1 DES does not exhibit blockage due to dependence on the binding protein that allows it to circulate. The circulation of IGF-1 DES is therefore free and available throughout the bloodstream waiting to find a receptor.
During physical efforts, a combustion is made at the level of the muscle thanks to oxygen and sugar. This creates ADP (Adenosine Di-phosphate) and then Lactic Acid.
The accumulation of lactic acid in the muscles causes a burning sensation and even cramps at higher doses. Moreover, this acid prevents the receptors from working properly. Some anabolic or anti-catabolic drugs will not find their receptor and will therefore not be able to act. This can happen with IGF-1, but not for IGF-1 DES which is receptor free.
IGF-1 DES is 100% bioavailable (because it is not bound to receptors), it is 10 times more anabolic than the IGF-1 created by the body and it has the advantage of being active even when lactic acid appears in the muscle tissue.
Many will regret that its life activity lasts only a few minutes.
